Infection with bacteria most often occurs through contact with a sick creature or any infected object. In addition, some bacterial infections carry parasites (ticks, fleas). Most ailments are treated with antibiotics prescribed by a doctor. But, in order to choose an effective treatment regimen, it is necessary to correctly identify the “culprit” and the type of disease.
Q fever, or coxiellosis (Q-febris)
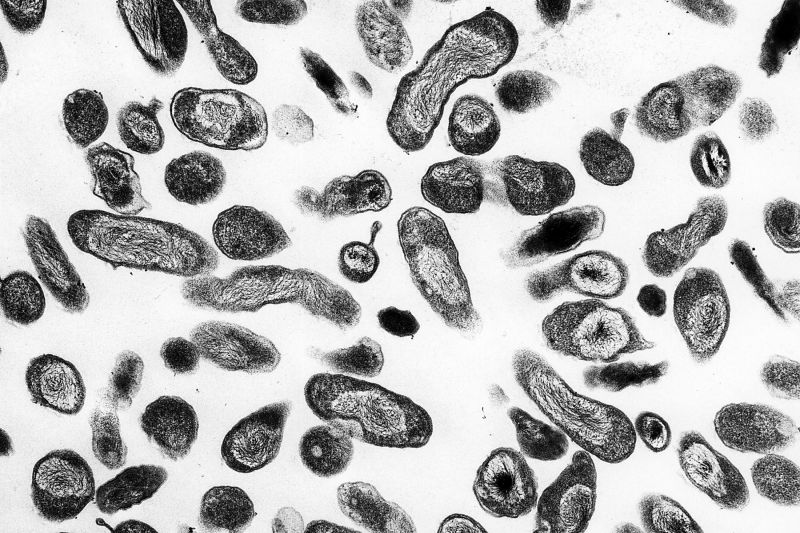
Not only mammals (including humans) are affected by this infection, but also birds. It is caused by the bacteria Coxiella burnetii, which infect the cells responsible for protecting the body.
In cats, Q fever almost does not occur. Sometimes there is a slight malaise, lack of appetite. Since these symptoms are very common, they are not always associated with coxiellosis. To a greater extent, the disease manifests itself after childbirth, when the body is weakened. Then the body temperature rises, weight decreases, coordination of movements is disturbed.
Human infection is unlikely. Currently, Q fever is not found everywhere, but, for example, in the United States, Australia, Greece, and the Netherlands. But when making such a diagnosis, it is better not to risk and isolate the pet for a while and treat it with antibiotics.
Nocardiosis
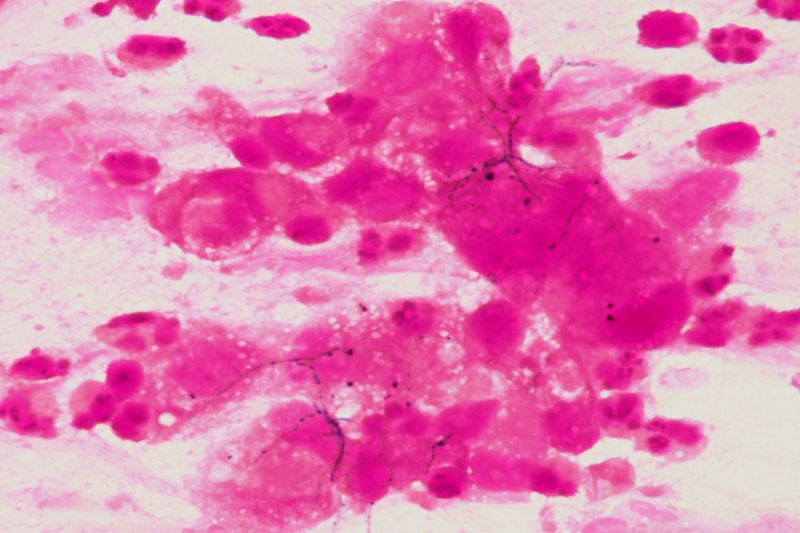
This bacterial disease usually proceeds in a chronic form. Unicellular microorganisms from the genus Nocardia penetrate through the respiratory system and skin. Nocardiosis does not have specific symptoms, most often the lymph nodes become inflamed, the mammary glands often suffer, a fungus appears on the skin (therefore, the disease is often confused with ordinary mycosis), which develops into ulcers.
Fortunately, nocardiosis is currently rare. It is difficult to treat. In addition to antibiotic therapy, surgical intervention may be required.
Lyme Disease, or Tick-borne Borreliosis
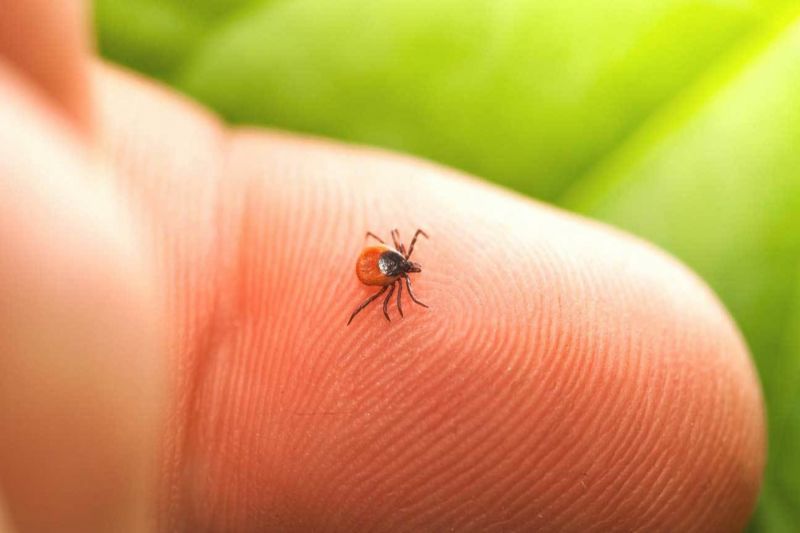

Ixodid ticks carry bacteria (spirochetes) from the genus Borrelia and infect them during a bite. Tick-borne borreliosis is dangerous not only for cats, but also for humans. At first, it is asymptomatic.
Some pets have redness at the site of the bite of an arthropod parasite, and sometimes appetite disappears. After a couple of months, signs such as:
joint damage (arthritis), lameness;
nervous disorders;
failure of internal organs (primarily the excretory system).
If treatment is not started immediately, Lyme borreliosis will result in death. Therefore, it is important to consult a veterinarian as quickly as possible. And in order to prevent infection, do not forget about prevention. If your cat is walking along the street, treat it with acaricidal agents from early spring to late autumn.
Yersiniosis
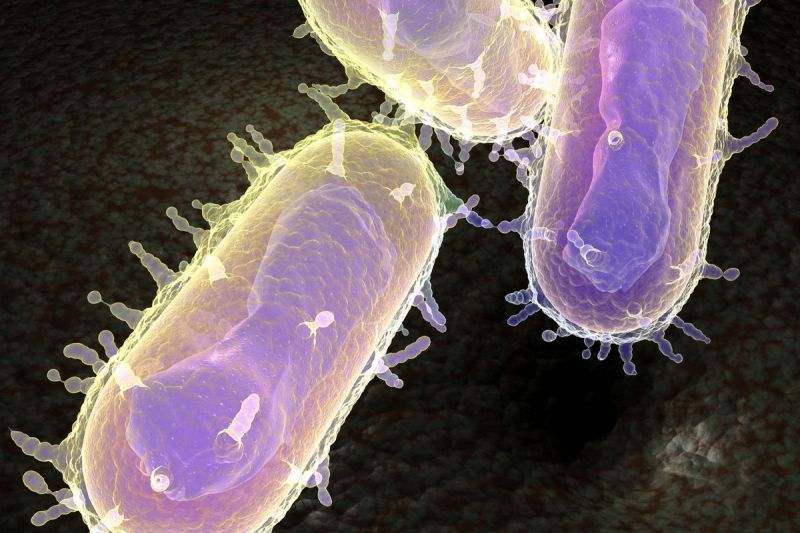
Yersiniosis is a disease caused by the bacteria Yersinia enterocolitica, which attack the gastrointestinal tract. Common symptoms are abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, skin rash. Without a shock dose of antibacterial drugs, yersiniosis cannot be cured.
Staphylococcosis
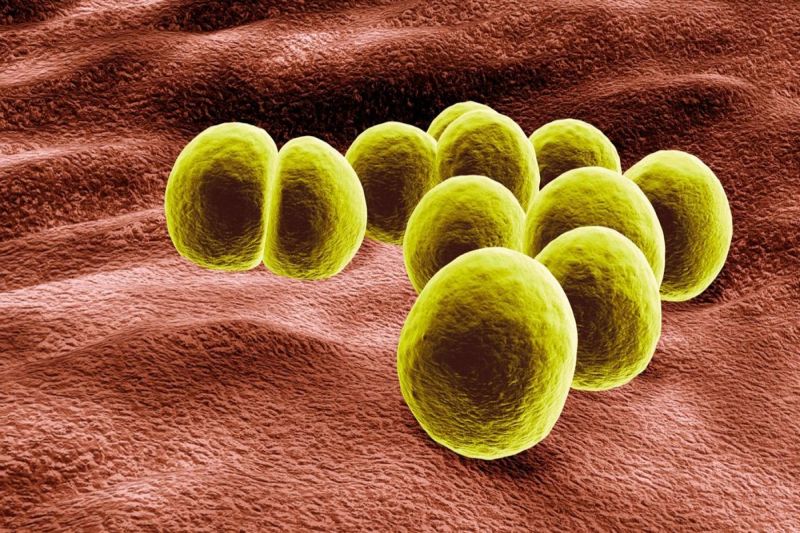
Infection with staphylococci is manifested by skin rashes, purulent erosion, itching, hair loss. Boils often form, other ailments “connect” (vaginitis, inflammation of the middle ear). Laboratory diagnosis is indispensable.
Today, these infections are rare in cats. Such diagnoses as salmonellosis, colibacillosis, tuberculosis, leprosy, mycetoma, etc. are even less often made. But warned - that means armed! Follow the health of the mustachioed pet and do not endanger his life.
 Select language
Select language 





.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)
